

















Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
Botrytis: The Fungus, The Pathogen, and Its Management in Agricultural Systems

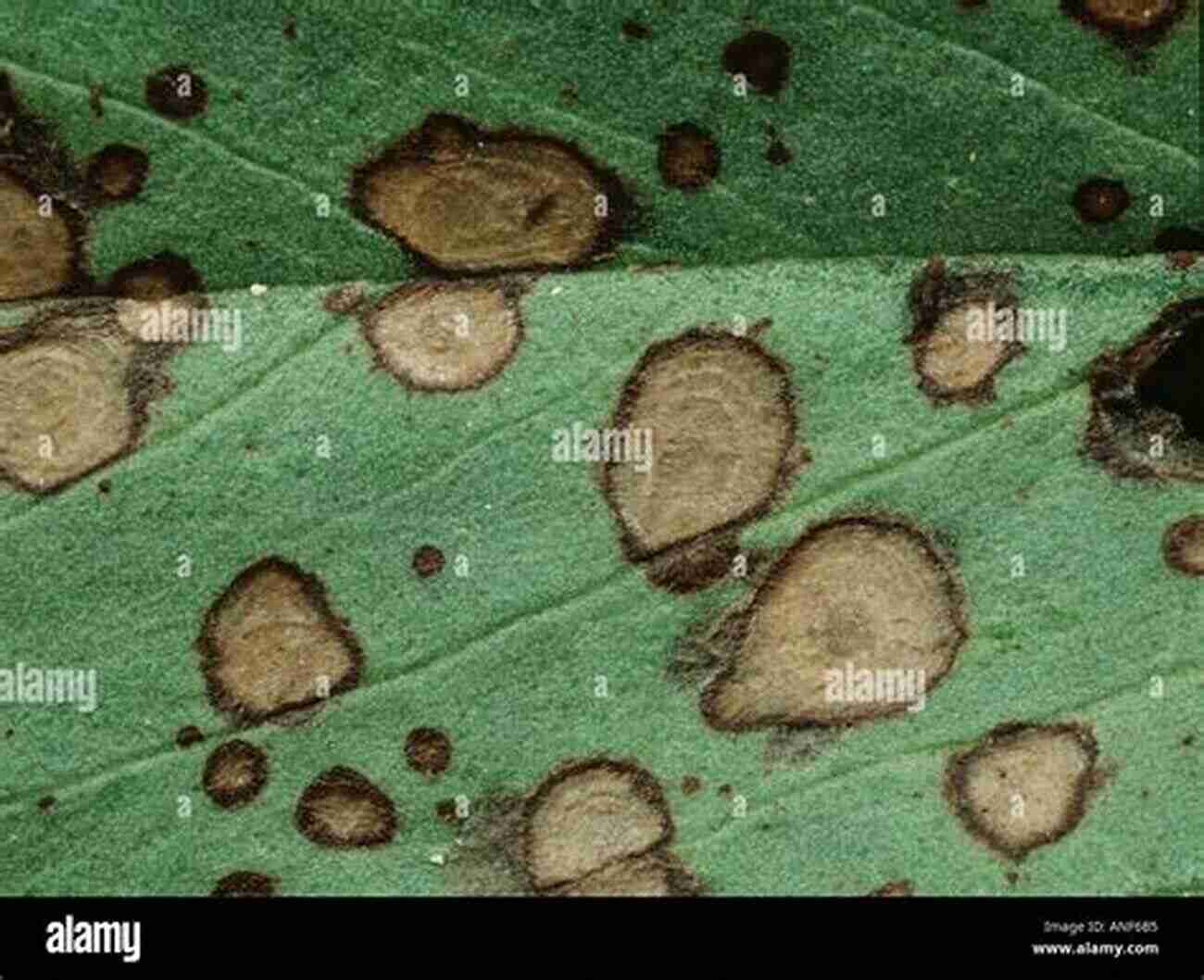
Botrytis, commonly known as gray mold, is a devastating fungus affecting numerous agricultural crops worldwide. Its ability to infect a wide range of plant species and its destructive nature make it a significant concern for farmers and agronomists. In this article, we will explore the characteristics of Botrytis, its pathogenicity, and effective management strategies to mitigate its impact on agricultural systems.
Understanding Botrytis
Botrytis belongs to the fungal genus Botrytis, specifically Botrytis cinerea, and is responsible for causing gray mold disease. This fungus thrives in cool and humid conditions, making it a prevalent pathogen in various regions. Its grayish appearance on infected plants is a result of the abundant gray spores produced during sporulation. The spores remain dormant until favorable environmental conditions trigger their germination and infection processes.
The life cycle of Botrytis involves several stages, including spore germination, mycelium development, and sporulation. Spores can be spread through wind, water, or via physical contact with infected plant material.
4.5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 6682 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 799 pages |
Pathogenicity of Botrytis
Botrytis infection starts when the fungal spores land on susceptible plant tissues. The spores penetrate the plant's surface, primarily through wounds or natural openings, such as stomata. Once inside the plant, Botrytis develops filamentous structures, known as hyphae, which invade the plant tissues and extract nutrients for its growth and reproduction.
The infection rapidly progresses, leading to the development of visible symptoms such as gray, fuzzy mold on the plant's surface, wilting, and decay. Botrytis can cause severe damage to various parts of the plant, including flowers, fruits, stems, and leaves.
Impact on Agricultural Systems
The presence of Botrytis in agricultural systems poses substantial risks to both crop quality and yield. It affects a wide range of economically important crops, including grapes, strawberries, lettuce, tomatoes, and many more. Infected fruits and vegetables often become unmarketable due to the presence of visible mold or rot. Additionally, gray mold can facilitate the entry of other pathogens, leading to secondary infections and further crop losses.
The economic consequences of Botrytis can be significant for farmers, as they may experience reduced profit margins and increased production costs due to intensive fungicide applications and crop losses.
Effective Management Strategies
Given the destructive nature of Botrytis, implementing effective management strategies is crucial to minimize its impact on agricultural systems. Here are some key approaches:
1. Cultural Practices
Implementing proper cultural practices, such as crop rotation, sanitation, and pruning, can significantly reduce Botrytis infection. Crop rotation disrupts the disease cycle by minimizing the accumulation of inoculum in the soil, while regular pruning improves airflow and reduces humidity, creating an unfavorable environment for the fungus.
Sanitation practices involve removing and destroying infected plant debris and providing appropriate disposal methods to prevent the spread of the pathogen to healthy plants.
2. Biological Control
Biological control methods focus on using beneficial microorganisms, such as certain strains of bacteria or fungi, to suppress Botrytis populations. These antagonistic organisms can outcompete the pathogen for resources or produce antifungal compounds that inhibit its growth.
Introducing beneficial insects, such as predatory mites or bugs, can also help control Botrytis by feeding on the fungal spores and reducing their population.
3. Chemical Control
Chemical control measures involve the use of fungicides to mitigate Botrytis infections. Fungicides can be applied preventively or curatively, depending on the severity of the disease. However, it is essential to use fungicides responsibly and follow recommended guidelines to minimize the development of resistance and reduce potential environmental impacts.
4. Genetic Resistance
Developing and utilizing crop varieties with genetic resistance to Botrytis is another promising approach in managing the pathogen. Breeders aim to incorporate resistance genes into commercially valuable cultivars to enhance their tolerance to gray mold disease.
By adopting an integrated approach that combines multiple management strategies, farmers can effectively control Botrytis and reduce its impact on agricultural systems.
Botrytis, the gray mold fungus, poses significant challenges to agricultural systems worldwide. Its destructive nature and ability to infect a wide range of crops necessitate comprehensive management strategies. By implementing cultural practices, biological control, chemical control, and genetic resistance, farmers can minimize the impact of Botrytis and protect their crops from severe losses. It is crucial for researchers, agronomists, and farmers to collaborate and continuously develop innovative approaches to combat this widespread pathogen.
References:
1. Smith, L. E., & Momol, M. T. (2015). Botrytis gray mold. Plant pathology fact sheet.
2. Elad, Y., et al. (2016). Botrytis spp. and diseases they cause in agricultural systems—an . Botrytis—the fungus, the pathogen and its management in agricultural systems.
Back to Top
4.5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 6682 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 799 pages |
The fungal genus Botrytis is the focus of intensive scientific research worldwide. The complex interactions between this pathogen and the plants it infects and the economic importance of the diseases caused by Botrytis (principally grey mould) on more than 1400 species of cultivated plants pre- and post-harvest, render this pathogen of particular interest to farmers, advisers, students and researchers in many fields worldwide. This 20-chapter book is a comprehensive treatise covering the rapidly developing science of Botrytis and reflecting the major developments in studies of this fungus. It will serve as a source of general information for specialists in agriculture and horticulture, and also for students and scientists interested in the biology of this fascinating, multifaceted phytopathogenic fungal species.

 Harrison Blair
Harrison BlairSoldiers League: The Story of Army Rugby League
The Origin and History The Soldiers...

 Bob Cooper
Bob CooperFilm Quiz Francesco - Test Your Movie Knowledge!
Are you a true movie buff? Do you...

 Hugh Reed
Hugh ReedDriving Consumer Engagement In Social Media
: Social media has...

 Richard Simmons
Richard SimmonsAll You Need To Know About The Pacific Ocean Ocean For...
The Pacific Ocean is the largest ocean in...

 Carson Blair
Carson BlairUnveiling the Intriguing World of Complex Wave Dynamics...
The study of complex wave...

 Connor Mitchell
Connor MitchellUnraveling the Mysterious Journey of "The Nurse And The...
Once upon a time, in a world of endless...

 Colt Simmons
Colt SimmonsHow To Change Your Child's Attitude and Behavior in Days
Parenting can be both challenging and...

 Reginald Cox
Reginald Cox10 Groundbreaking Contributions Through Science And...
Science and technology have always...

 Ernesto Sabato
Ernesto SabatoUnleashing the Power of Hamilton Education Guides Manual...
Are you struggling with understanding...

 Virginia Woolf
Virginia WoolfThe Astonishing Tale of Mars: Lord of the Dragon Throne -...
There has always been a remarkable...

 Colt Simmons
Colt SimmonsAn Introduction For Scientists And Engineers Second...
Are you a budding scientist or engineer...

 Howard Blair
Howard BlairDiscover the Coolest and Trendiest Friendship Bracelets -...
Friendship bracelets have...
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Julio Ramón RibeyroThe Extraordinary Journey of Boris Malomed: Unraveling the Legacy of Loud And...
Julio Ramón RibeyroThe Extraordinary Journey of Boris Malomed: Unraveling the Legacy of Loud And...
 Michael CrichtonDiscover How Phosphoric Acid Purification Revolutionizes Industries - Its...
Michael CrichtonDiscover How Phosphoric Acid Purification Revolutionizes Industries - Its...
 Brennan Blair10 Essential Security Measures to Safeguard Museums, Libraries, Parks, and...
Brennan Blair10 Essential Security Measures to Safeguard Museums, Libraries, Parks, and... Roald DahlFollow ·3.1k
Roald DahlFollow ·3.1k Ken SimmonsFollow ·14.1k
Ken SimmonsFollow ·14.1k Darrell PowellFollow ·7.8k
Darrell PowellFollow ·7.8k Guillermo BlairFollow ·7.4k
Guillermo BlairFollow ·7.4k Dale MitchellFollow ·15.5k
Dale MitchellFollow ·15.5k Carlos FuentesFollow ·7.2k
Carlos FuentesFollow ·7.2k Jarrett BlairFollow ·10k
Jarrett BlairFollow ·10k Floyd PowellFollow ·4.6k
Floyd PowellFollow ·4.6k
















