















Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
Experience the Fascinating World of Classical Approach To Constrained And Unconstrained Molecular Dynamics!

Are you ready to dive deep into the captivating realm of molecular dynamics? Prepare to be amazed as we unravel the classical approach to constrained and unconstrained molecular dynamics. In this comprehensive article, we will explore the inner workings and applications of this intriguing field.
Understanding Molecular Dynamics
Molecular dynamics is a powerful computational technique used to study the behavior and motion of molecules over time. By simulating the interactions between atoms and molecules at the atomic level, scientists gain valuable insights into various biological and chemical processes.
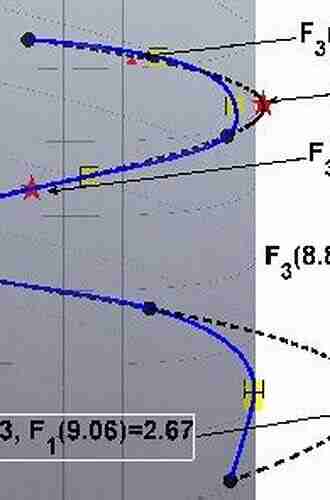
Classical molecular dynamics employs Newton's second law of motion to determine the trajectories of particles under the influence of interatomic forces. By integrating the equations of motion, scientists can simulate the movement of molecules in a time-dependent manner.
4.7 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 5618 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Print length | : | 146 pages |
| X-Ray for textbooks | : | Enabled |
Constrained Molecular Dynamics
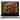
Constrained molecular dynamics focuses on studying systems where certain constraints or restrictions are imposed on the molecules. These constraints can arise from various factors, such as experimental observations or theoretical considerations. By incorporating these constraints into the simulation, scientists can accurately model real-world scenarios.
One common type of constraint is the imposition of fixed bond lengths or bond angles. For example, in a protein molecule, the backbone atoms are connected by covalent bonds with specific characteristic lengths and angles. Constrained dynamics allows researchers to study how the system behaves while maintaining these structural properties.
Another example of constrained molecular dynamics is the simulation of systems under external spatial restraints. These restraints can be used to mimic the effects of experimental techniques like nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) or X-ray crystallography. By incorporating the experimental data as constraints, scientists can refine their models and improve the accuracy of their simulations.
Unconstrained Molecular Dynamics
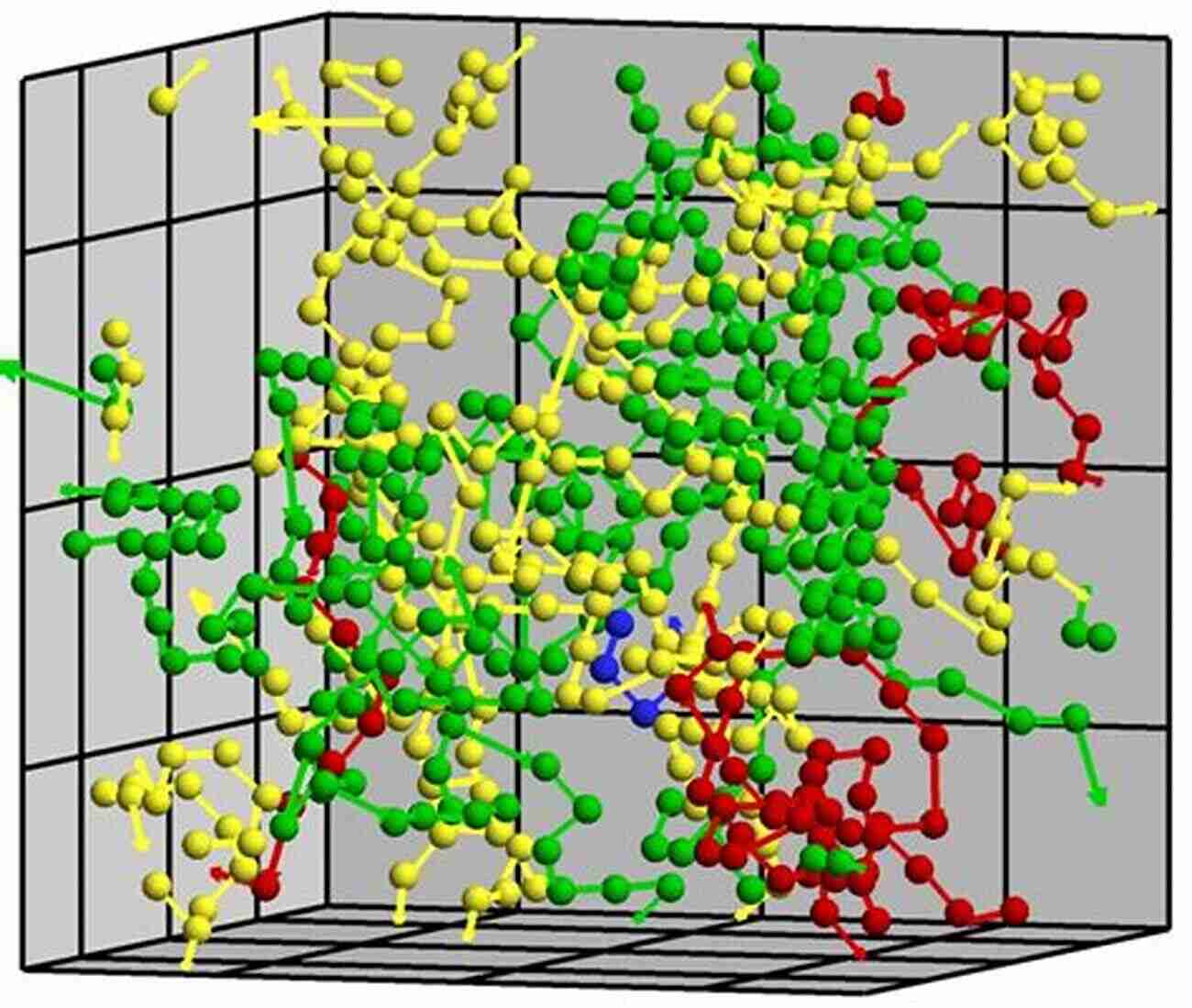
On the other hand, unconstrained molecular dynamics removes any constraints or restrictions from the simulation. This approach allows the molecules to freely explore their energy landscape, revealing valuable information about their conformational changes, dynamics, and thermodynamic properties.
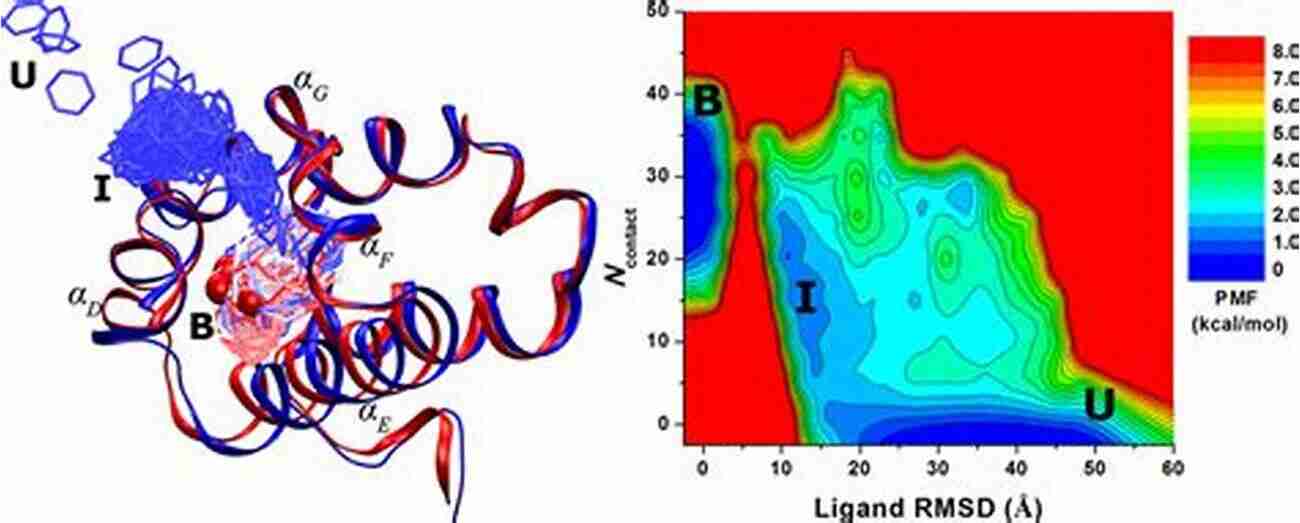
Unconstrained dynamics is often used to study large-scale biological systems such as proteins, nucleic acids, and lipid membranes. By simulating the dynamics of these complex systems, scientists gain crucial insights into the mechanisms underlying various biological processes, including protein folding, enzymatic reactions, and drug binding.
Applications and Advancements
The classical approach to molecular dynamics has revolutionized many fields of research. Its applications are far-reaching, spanning from drug discovery and design to materials science and nanotechnology.
In drug discovery, molecular dynamics simulations help scientists understand the interactions between drugs and target proteins at an atomic level. By simulating the binding process, researchers can optimize drug molecules for better efficacy and reduce potential side effects.
In materials science, molecular dynamics simulations allow scientists to investigate the mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties of materials. This knowledge is vital for designing new materials with enhanced functionalities, such as superior strength, improved thermal conductivity, or higher electrical conductivity.
The continuous advancement in computational power has made it possible to simulate more complex systems, longer timescales, and finer details. Coupled with the development of accurate force fields and efficient algorithms, classical molecular dynamics simulations continue to provide valuable insights into the behavior of molecules and materials.
The classical approach to constrained and unconstrained molecular dynamics is an indispensable tool in scientific research. By simulating the motion and behavior of molecules, scientists can unlock the mysteries of biological and chemical phenomena.
From exploring the mechanisms of protein folding to designing new drugs and materials, molecular dynamics opens up a world of possibilities for scientific advancements. So, fasten your seatbelts and embark on an exhilarating journey into the captivating realm of classical molecular dynamics!
4.7 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 5618 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Print length | : | 146 pages |
| X-Ray for textbooks | : | Enabled |
In this book, we propose a penalty-function method for constrained molecular dynamics simulation by defining a quadratic penalty function for the constraints. The simulation with such a method can be done by using a conventional, unconstrained solver only with the penalty parameter increased in an appropriate manner as the simulation proceeds. More specifically, we scale the constraints with their force constants when forming the penalty terms.

 Harrison Blair
Harrison BlairSoldiers League: The Story of Army Rugby League
The Origin and History The Soldiers...

 Bob Cooper
Bob CooperFilm Quiz Francesco - Test Your Movie Knowledge!
Are you a true movie buff? Do you...

 Hugh Reed
Hugh ReedDriving Consumer Engagement In Social Media
: Social media has...

 Richard Simmons
Richard SimmonsAll You Need To Know About The Pacific Ocean Ocean For...
The Pacific Ocean is the largest ocean in...

 Carson Blair
Carson BlairUnveiling the Intriguing World of Complex Wave Dynamics...
The study of complex wave...

 Connor Mitchell
Connor MitchellUnraveling the Mysterious Journey of "The Nurse And The...
Once upon a time, in a world of endless...

 Colt Simmons
Colt SimmonsHow To Change Your Child's Attitude and Behavior in Days
Parenting can be both challenging and...

 Reginald Cox
Reginald Cox10 Groundbreaking Contributions Through Science And...
Science and technology have always...

 Ernesto Sabato
Ernesto SabatoUnleashing the Power of Hamilton Education Guides Manual...
Are you struggling with understanding...

 Virginia Woolf
Virginia WoolfThe Astonishing Tale of Mars: Lord of the Dragon Throne -...
There has always been a remarkable...

 Colt Simmons
Colt SimmonsAn Introduction For Scientists And Engineers Second...
Are you a budding scientist or engineer...

 Howard Blair
Howard BlairDiscover the Coolest and Trendiest Friendship Bracelets -...
Friendship bracelets have...
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Fyodor DostoevskyJohn Stark Maverick General Paul Finkelman - The Bravery that Changed History
Fyodor DostoevskyJohn Stark Maverick General Paul Finkelman - The Bravery that Changed History E.M. ForsterFollow ·5.6k
E.M. ForsterFollow ·5.6k Junichiro TanizakiFollow ·6k
Junichiro TanizakiFollow ·6k Ross NelsonFollow ·9.9k
Ross NelsonFollow ·9.9k Jared PowellFollow ·17.6k
Jared PowellFollow ·17.6k Robert FrostFollow ·8.5k
Robert FrostFollow ·8.5k Julio CortázarFollow ·4.1k
Julio CortázarFollow ·4.1k Easton PowellFollow ·5.9k
Easton PowellFollow ·5.9k Gary ReedFollow ·4.4k
Gary ReedFollow ·4.4k