

















Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
The Site Reliability Engineer: Mastering the Art of Infrastructure Stability

In today's digital world, where companies rely heavily on their online presence, site reliability has become a crucial aspect of maintaining a successful business. This responsibility falls on the shoulders of the Site Reliability Engineer (SRE) - the unsung hero behind the scenes.
Who is a Site Reliability Engineer?
A Site Reliability Engineer is a professional responsible for ensuring the reliability and stability of websites, applications, and infrastructure. These experts bridge the gap between software development and operations, focusing on eliminating inefficiencies and creating systems that are resilient, scalable, and highly available.
The Responsibilities of an SRE
The responsibilities of an SRE are wide-ranging and essential to the success of any digital platform. Some of the primary tasks include:
4.2 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 7242 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Lending | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 160 pages |
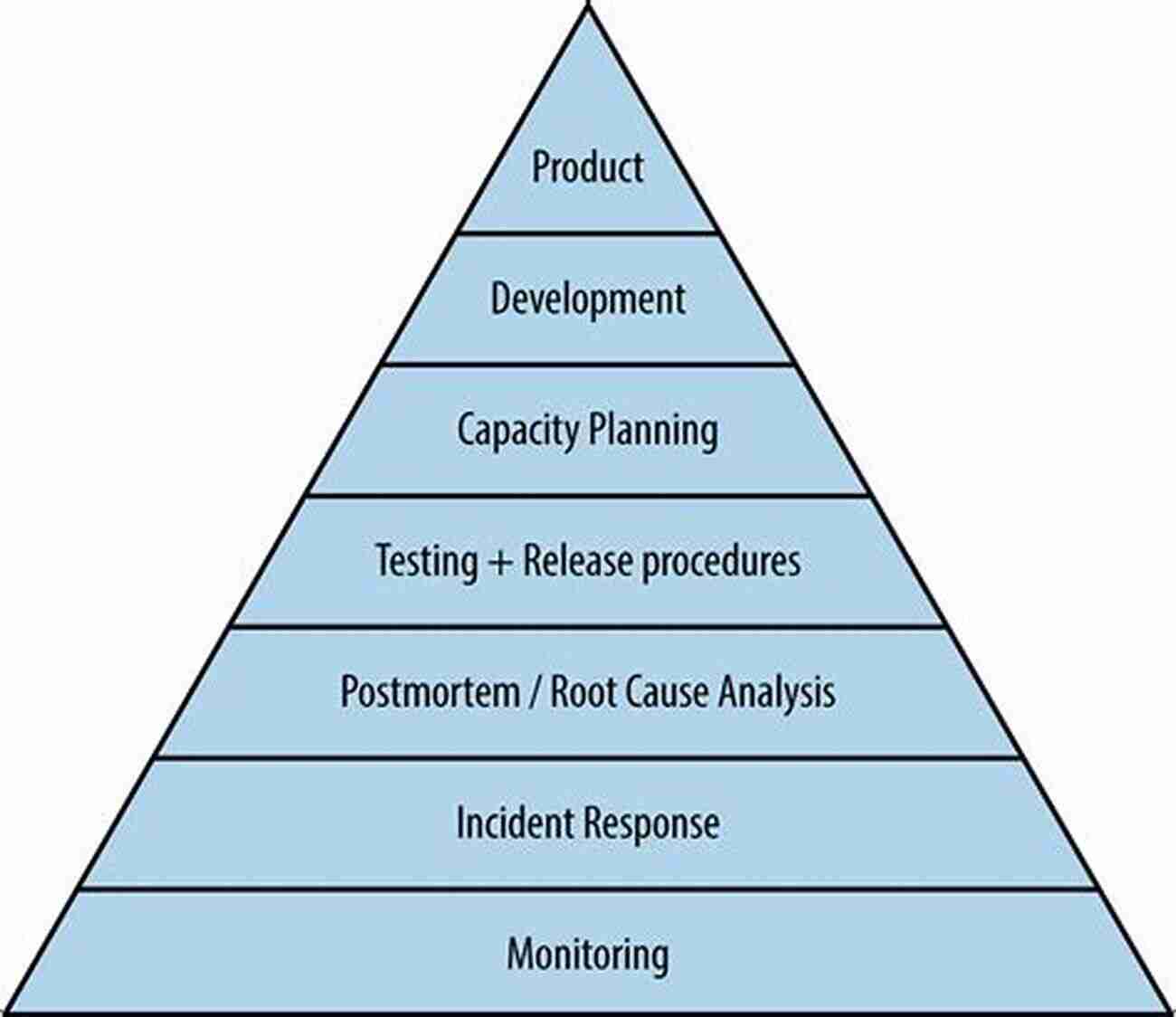
- Designing and implementing monitoring systems to track the health of the infrastructure
- Establishing and enforcing service-level objectives (SLOs)
- Developing automated processes for deployment and infrastructure management
- Performing capacity planning to ensure optimal performance and scalability
- Conducting post-incident reviews to identify areas for improvement
- Collaborating with development teams to enhance system reliability
The Essential Skills of an SRE
Becoming a successful SRE requires a diverse skill set and a deep understanding of both software development and operations. Some of the key skills include:
- Strong programming skills in languages such as Python, Go, or Java
- Expertise in various tools and technologies like Kubernetes, Docker, and AWS
- In-depth knowledge of networking, databases, and system administration
- Ability to analyze complex systems and troubleshoot issues efficiently
- Experience with configuration management tools such as Ansible or Puppet
- Excellent communication and collaboration skills to work effectively in cross-functional teams
The Benefits of Hiring an SRE
The role of an SRE goes beyond just ensuring the stability of a website or application. By investing in an SRE, organizations can experience numerous benefits:
- Improved reliability and uptime, minimizing costly downtime
- Enhanced scalability, allowing businesses to handle increased user demand without disruptions
- Reduced time-to-market, as automated processes enable faster deployments
- Greater cost-efficiency, optimizing resource allocation and infrastructure usage
- Better incident response and disaster recovery capabilities through meticulous planning
- Continuous improvement and innovation, fostering a culture of learning and evolving
The Future of Site Reliability Engineering
As digital infrastructure continues to grow in complexity, the importance of SREs will only increase. The future of Site Reliability Engineering holds exciting possibilities:
- Expansion into new domains like Internet of Things (IoT) and Edge Computing
- Integration of machine learning and artificial intelligence for predictive analysis
- Increased focus on building secure and resilient architectures
- Evolution of SRE practices to adapt to emerging technologies and paradigms
The Site Reliability Engineer plays an indispensable role in ensuring the stability, reliability, and scalability of digital platforms. Their expertise and skills are vital for businesses to stay competitive in the rapidly evolving digital landscape. By embracing the art of infrastructure stability, the modern SRE is at the forefront of innovation, excellence, and continuous improvement.
4.2 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 7242 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Lending | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 160 pages |
With the growing complexity of application development, organizations are increasingly adopting methodologies that enable reliable, scalable software.
DevOps and site reliability engineering (SRE) are two approaches that enhance the product release cycle through enhanced collaboration, automation, and monitoring. Both approaches utilize automation and collaboration to help teams build resilient and reliable software—but there are fundamental differences in what these approaches offer and how they operate.
So, this article delves into the purpose of DevOps and SRE. We’ll look at both approaches, including benefits, differences, and key elements.
Site reliability engineering (SRE)
SRE provides a unique approach to application lifecycle and service management by incorporating various aspects of software development into IT operations.
SRE was first developed in 2003 to create IT infrastructure architecture that meets the needs of enterprise-scale systems. With SRE, IT infrastructure is broken down into basic, abstract components that can be provisioned with software development best practices. This enables teams to use automation to solve most problems associated with managing applications in production.
SRE uses three Service Level Commitments to measure how well a system performs:
- Service level agreements (SLAs) define the required reliability, performance, and latency of the system as desired by end users.
- Service level objectives (SLOs) target values and goals set by SRE teams that should be met to satisfy SLAs.
- Service level indicators (SLIs) measure specific metrics and aspects that show how much a system conforms to the SLOs. Typical SLIs include request latency, system throughput, lead time, development frequency, mean time to restore (MTTR),and availability error rate.
:
The Site Reliability Engineer role
SRE essentially creates a new role: the site reliability engineer. An SRE is tasked with ensuring seamless collaboration between IT operations and development teams through the enhancement and automation of routine processes. Some core responsibilities of an SRE include:
- Developing, configuring, and deploying software to be used by operations teams
- Handling support escalation issues
- Conducting and reporting on incident reviews
- Developing system documentation
- Change management
- Determining and validating new features and updates

 Harrison Blair
Harrison BlairSoldiers League: The Story of Army Rugby League
The Origin and History The Soldiers...

 Bob Cooper
Bob CooperFilm Quiz Francesco - Test Your Movie Knowledge!
Are you a true movie buff? Do you...

 Hugh Reed
Hugh ReedDriving Consumer Engagement In Social Media
: Social media has...

 Richard Simmons
Richard SimmonsAll You Need To Know About The Pacific Ocean Ocean For...
The Pacific Ocean is the largest ocean in...

 Carson Blair
Carson BlairUnveiling the Intriguing World of Complex Wave Dynamics...
The study of complex wave...

 Connor Mitchell
Connor MitchellUnraveling the Mysterious Journey of "The Nurse And The...
Once upon a time, in a world of endless...

 Colt Simmons
Colt SimmonsHow To Change Your Child's Attitude and Behavior in Days
Parenting can be both challenging and...

 Reginald Cox
Reginald Cox10 Groundbreaking Contributions Through Science And...
Science and technology have always...

 Ernesto Sabato
Ernesto SabatoUnleashing the Power of Hamilton Education Guides Manual...
Are you struggling with understanding...

 Virginia Woolf
Virginia WoolfThe Astonishing Tale of Mars: Lord of the Dragon Throne -...
There has always been a remarkable...

 Colt Simmons
Colt SimmonsAn Introduction For Scientists And Engineers Second...
Are you a budding scientist or engineer...

 Howard Blair
Howard BlairDiscover the Coolest and Trendiest Friendship Bracelets -...
Friendship bracelets have...
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Herbert CoxThe Ultimate Guide to Judging Hunters And Hunter Seat Equitation: Unveiling...
Herbert CoxThe Ultimate Guide to Judging Hunters And Hunter Seat Equitation: Unveiling...
 Jay SimmonsUnveiling the Mysteries of Electromagnetic Fields and Interactions: Blaisdell...
Jay SimmonsUnveiling the Mysteries of Electromagnetic Fields and Interactions: Blaisdell...
 Roland HayesUnleash Your Potential: Mastering Cricket Bowling at Crickiteacher Primary...
Roland HayesUnleash Your Potential: Mastering Cricket Bowling at Crickiteacher Primary... William GoldingFollow ·2k
William GoldingFollow ·2k Hunter MitchellFollow ·13.3k
Hunter MitchellFollow ·13.3k Jett PowellFollow ·7.3k
Jett PowellFollow ·7.3k Kazuo IshiguroFollow ·17.4k
Kazuo IshiguroFollow ·17.4k Shannon SimmonsFollow ·8.6k
Shannon SimmonsFollow ·8.6k Jake CarterFollow ·10.1k
Jake CarterFollow ·10.1k Dan HendersonFollow ·12.1k
Dan HendersonFollow ·12.1k Neil GaimanFollow ·12.1k
Neil GaimanFollow ·12.1k
















